Oil Crops Research Institute Revealed the Dietary Preventive Effects and Mechanisms of Gout and Rheumatoid Arthritis
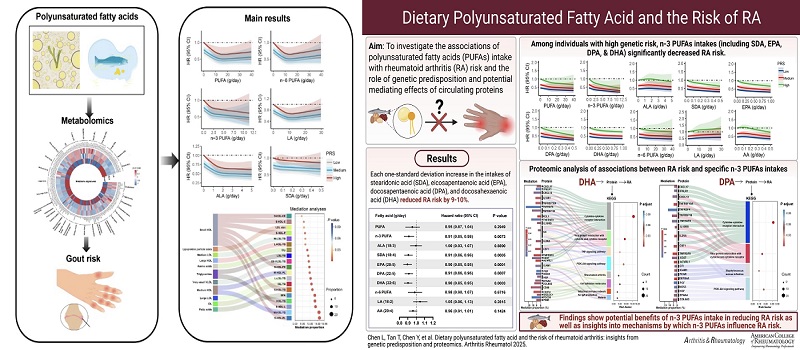
Recently, the Oil Quality Chemistry and Processing Utilization Innovation Team of the Oil Crops Research Institute, in collaboration with the School of Public Health of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, published a series of studies indicating that n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce the risk of gout and rheumatoid arthritis and the mechanism of action. These findings provide a scientific foundation for dietary strategies in preventing above conditions The relevant achievements were published in the international authoritative academic journals "European Journal of Epidemiology" and "Arthritis & Rheumatology".
N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are widely present in foods such as vegetable oils and fish, and have functions such as anti-inflammation and regulating lipid metabolism.Through cohort studies, metabolomics, proteomics and mediation analysis, the team found that n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduced the risk of gout and rheumatoid arthritis by regulating plasma metabolites and protein levels. Especially, alpha-linolenic acid from plant sources, for every 0.8 grams increase in intake, the incident risk of gout was reduced by 8%. Marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, for every 0.2-0.3 grams increase in intake, reduced the risk of rheumatoid arthritis by 9%-10%. According to experts, plant-derived alpha-linolenic acid is found in flaxseeds, perilla seeds, and rapeseeds, while marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are present in marine fish, seaweeds, and microalgae.
The above-mentioned research was supported by the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System and the Innovation Group Project of Hubei Province.
Link:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10654-025-01242-9
https://acrjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.43229